Alibaba History: From Humble Beginnings to Global E-Commerce Giant

Alibaba has emerged as one of the most influential players in the e-commerce industry, revolutionizing the way people buy and sell goods and services. By exploring the timeline of Alibaba's development, the pivotal role played by its founder, Jack Ma, and the significant milestones along the way, we gain a comprehensive understanding of how this company has shaped the e-commerce landscape.
This article provides an in-depth look into the journey of Alibaba, tracing its growth from its humble beginnings to becoming a global e-commerce giant.
Alibaba's Timeline
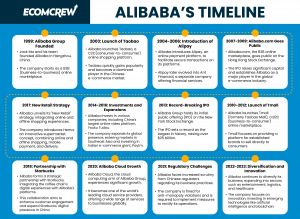
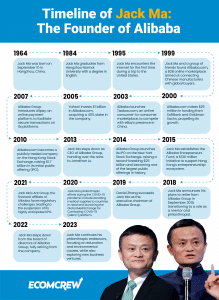
Foundational Years (1999-2004)
Alibaba was established by Jack Ma and his co-founders with a vision to connect Chinese manufacturers with international buyers. They recognized the untapped potential of the internet and set out to create an online marketplace. In 1999, Alibaba.com was launched, serving as a platform for business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce.
This marked the beginning of Alibaba's operations and its mission to empower small businesses through technology. Additionally, Alibaba introduced its first major platforms, including Taobao, an online shopping platform, and Alipay, a secure payment system, both of which laid the foundation for the company's future success.
Expanding Domestically and Globally (2005-2010)
In the following years, Alibaba focused on expanding its reach within China and venturing into the international market. The company introduced innovative services such as Alibaba Cloud, an advanced cloud computing platform, and AliExpress, an online retail marketplace catering to international customers.
Moreover, Alibaba made strategic acquisitions, including the renowned online auction platform, Taobao, and the leading online payment provider, Alipay. These initiatives bolstered Alibaba's presence both domestically and globally, solidifying its position as a key player in the e-commerce industry.
Diversification and IPO (2011-2014)
Driven by a vision of diversification, Alibaba made significant strides in various industries and sectors. It ventured into areas such as logistics, digital entertainment, and financial services, broadening its ecosystem and offering a comprehensive range of products and services.
In 2014, Alibaba made headlines with its record-breaking initial public offering (IPO) on the New York Stock Exchange. The IPO marked a significant milestone, as it showcased Alibaba's immense growth and potential, attracting global attention and cementing its status as a powerhouse in the e-commerce industry.

Continued Growth and Innovation (2015-2021)
From 2015 to 2021, Alibaba continued to expand its ecosystem and innovate its services. The company invested in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and big data analytics, integrating them into its platforms to enhance user experiences and streamline operations.
Alibaba also forged strategic partnerships with industry leaders, including major global brands and influential tech companies, to foster collaboration and drive further growth. These efforts propelled Alibaba's continued success and reaffirmed its position as a trailblazer in the e-commerce landscape.
The Founder: Jack Ma
To truly understand Alibaba's journey, it is essential to delve into the life of its visionary founder, Jack Ma.
Born in Hangzhou, China, Jack Ma grew up in modest surroundings. He encountered numerous challenges and rejections throughout his early life but remained determined to overcome them. Jack Ma's educational journey included studying English at Hangzhou Normal University, where he developed a passion for entrepreneurship.
The inception of Alibaba was driven by Jack Ma's desire to create opportunities for small businesses in China. After witnessing the immense success of e-commerce during a trip to the United States, Ma was inspired to establish an online platform that would bridge the gap between Chinese manufacturers and global buyers.
Securing funding for Alibaba presented its own set of challenges. In the early stages, investors were skeptical about the potential of e-commerce in China and were reluctant to invest. Jack Ma and his team faced numerous rejections, but their unwavering determination led them to secure early funding from a group of visionary investors. Over time, Alibaba attracted notable investors and underwent multiple funding rounds, enabling the company to fuel its growth and further solidify its position as a market leader.
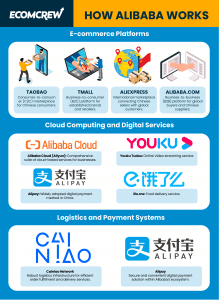
How Alibaba Works
Here are the key components of Alibaba's business model, its popular platforms such as Alibaba.com, Taobao, Tmall, and the innovative technologies that drive its success.
1. E-commerce Platforms
Alibaba operates through several key e-commerce platforms that cater to different segments of the market. Taobao, Alibaba's flagship platform, is a consumer-to-consumer (C2C) marketplace that offers a wide range of products and services to Chinese consumers.
Tmall, on the other hand, focuses on business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions, providing a platform for established brands and retailers to reach a vast customer base.
Another Alibaba-owned platform is AliExpress. It serves as an international marketplace, connecting Chinese sellers with customers worldwide.
2. Cloud Computing and Digital Services
Alibaba Cloud, also known as Aliyun, is Alibaba's cloud computing arm, offering a comprehensive suite of cloud-based services. It provides scalable computing power, storage solutions, and data analytics capabilities to businesses of all sizes, enabling them to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and accelerate innovation.
In addition to cloud computing, Alibaba offers a range of digital services, including online video streaming (Youku Tudou), digital payments (Alipay), food delivery (Ele.me), and more. These services further extend Alibaba's reach and contribute to its ecosystem of interconnected offerings.
3. Logistics and Payment Systems
To support its vast e-commerce operations, Alibaba has established a robust logistics infrastructure through Cainiao Network.
Cainiao collaborates with logistics partners to facilitate efficient order fulfillment, package tracking, and delivery services. By integrating various logistics providers, Cainiao optimizes the supply chain, enabling Alibaba and its merchants to offer fast and reliable shipping options.

Furthermore, Alibaba's payment system, Alipay, has become a widely adopted digital payment method in China. It offers secure and convenient payment solutions for online and offline transactions, facilitating seamless financial transactions within Alibaba's ecosystem.
Alibaba’s Challenges with the Chinese Government
Alibaba has encountered regulatory scrutiny, antitrust investigations, and a shift in government policies that have impacted its operations. These challenges have raised concerns about the company's future prospects and its ability to navigate the complex regulatory landscape in China.
- Government Regulations and Compliance. As Alibaba grew, it faced heightened scrutiny and regulatory challenges from the Chinese government. When Jack Ma challenged the government, he briefly disappeared from the public view, leading to rumors of his demise.
The government implemented stricter regulations for consumer protection, fair competition, and data privacy. Alibaba had to adapt to comply, navigating the complex regulatory landscape with constant monitoring and adjustments.
- Antitrust Investigations and Fines. In 2021, China fined Alibaba $2.8 billion in a landmark antitrust case. The company faced investigations by Chinese regulatory authorities focusing on alleged monopolistic practices and anti-competitive behavior. Consequently, Alibaba had to implement measures to address the identified issues.
The significant fine and investigations had a profound impact on Alibaba's reputation, operations, and market value, underscoring the vital importance of compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Conclusion
Alibaba's journey from its humble beginnings to becoming a global e-commerce giant has left an indelible mark on the industry. By understanding the workings of Alibaba's e-commerce platforms, cloud computing services, logistics infrastructure, and payment systems, we gain insights into the mechanisms that have contributed to its success.
However, Alibaba has also faced challenges, including navigating government regulations and compliance requirements, as well as dealing with antitrust investigations and fines. Despite these obstacles, Alibaba's impact on the e-commerce landscape remains undeniable.
By reflecting on Alibaba's history, we can draw valuable lessons and perspectives for future developments in the ever-evolving world of e-commerce.



welldone for insightful,educative,highly enriching article.