A Beginner’s Guide to E-Commerce

Currently, there are approximately 2.14 billion online customers worldwide and around 12 to 24 million sellers that own e-commerce sites, the latter growing in number daily. E-commerce sells almost all imaginable products and services there are.
But what is e-commerce, exactly? This article will teach you all you need to know about e-commerce, including its history, its pros and cons, how it’s affecting traditional stores, and how you can start as an online seller.
What Is E-commerce?
E-commerce or “electronic commerce” is the process of trading tangible goods and services online. Transactions can be conducted on any smart device, such as computers, smartphones, and tablets. Some e-commerce businesses only sell online, while others use physical stores and other distribution channels as well.
Think of Amazon, Shopify, Temu, Alibaba, and other marketplaces. They are all involved in e-commerce.
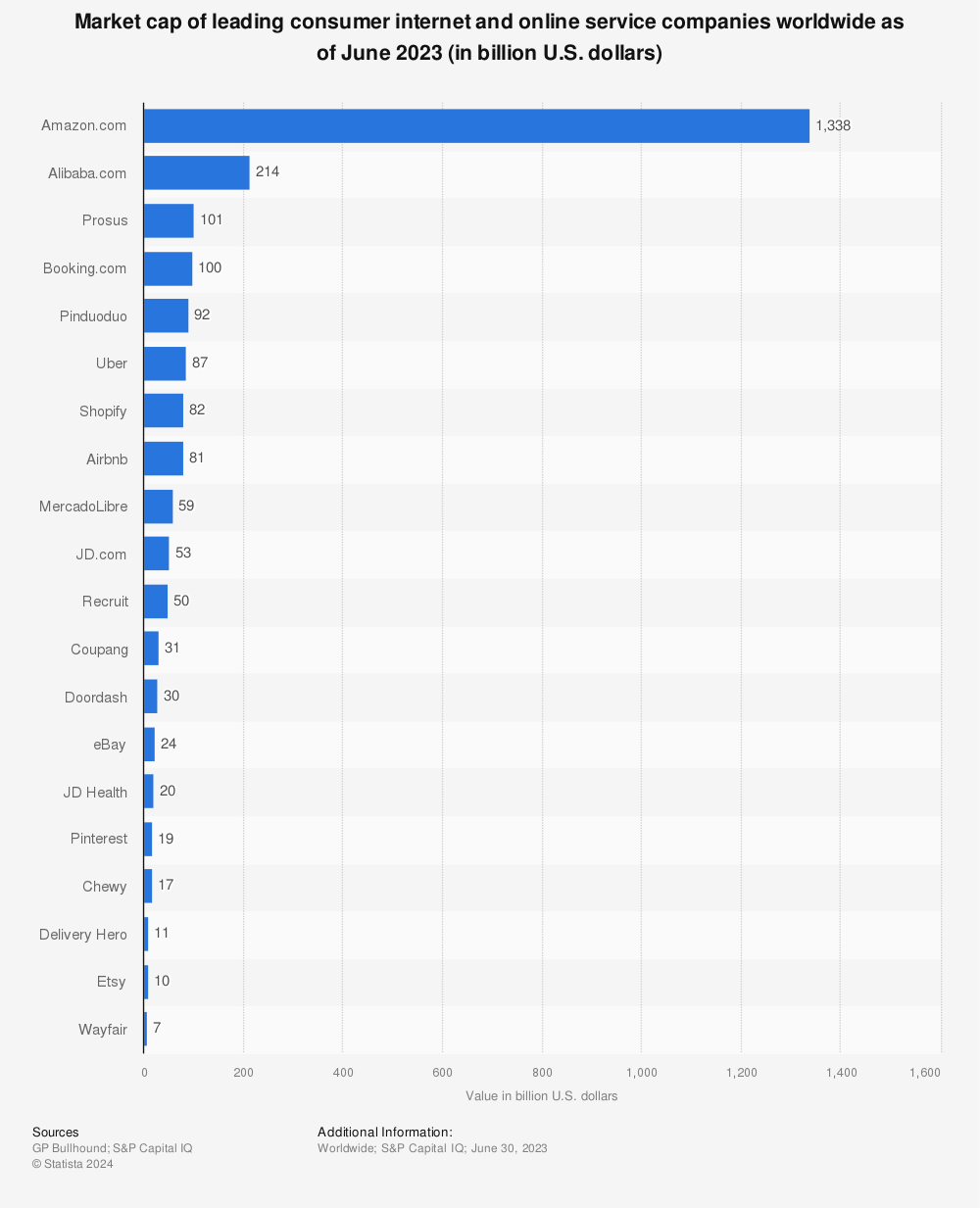
The popularity of e-commerce brought about the rise of online selling platforms. Source: Statista
An e-commerce business is just a part of a bigger industry called electronic business (e-business), which encompasses all online company operations and processes.
An e-commerce business generates income from selling products or services online, anything from books, music, financial services, housewares, software, and apparel, to web design services. E-commerce businesses use online channels such as marketplaces like Amazon, dedicated sites, social media platforms, and email.
Every e-commerce website is basically an online seller’s digital storefront where every transaction is made. The website serves as the virtual space where sellers display their products, customers make choices and acts as sales staff and cash register of the business all in one.
Sellers can create their online stores on Amazon, Shopify, Walmart, eBay, or other marketplace platforms, develop their website with their own domain, use social media channels, or apply all these for a broader business strategy. E-commerce overall enables every business, whether startups, small, or large, to reach customers and sell at a greater scale across the globe.
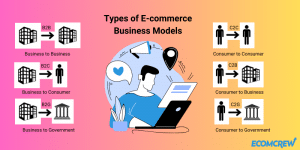
E-commerce businesses or individuals can operate in different market segments or types. Here are the most common business models:
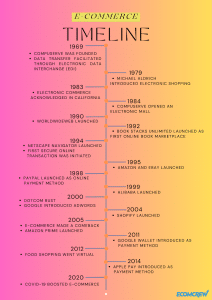
How E-commerce Started: History and Timeline
E-commerce began long before the Internet existed. It started back in the 1960s when CompuServe was founded and companies used the Electronic Data Interchange, which is an electronic system that facilitates document transfers.
Upon the introduction of the internet, CompuServe was not really used for selling things over the internet, just by theory. It was only in 1994 when the very first secure online transaction was initiated, involving the sale of a CD between friends using NetMarket, an online retail website.
How Does E-commerce Work?
E-commerce is all about connecting buyers and sellers through various online channels, including e-commerce website, social media platforms, or email. Through these platforms, customers can make selections on which products and services to buy and pay through an online payment method.
After a successful transaction, the customer will receive a confirmation via email, SMS, or on the marketplace app itself. They will also get a digital receipt and a tracking number.
Aside from the e-commerce business types, there are also various revenue models in which the business will make money.
What Are the Pros and Cons of E-commerce?
Running an online business can be lucrative, especially because a lot of its aspects may be automated. However, it has its own disadvantages. Here are some factors you have to consider to see if e-commerce will work for you:
Pros
- Rapid growth
- Global marketing reach
- International Sales
- Ease of ordering products
- Lower operating costs
- Direct-to-consumer access
- Easy to retarget customers
- Open 24/7
- Increased selection
Cons
- Limited face-to-face interaction or customer service
- Technical difficulties
- Data security concerns
- Shipping and fulfillment scale
- Heavy reliance on technology
- Shipping constraints
How Does E-commerce Affect Traditional Stores?
Traditional stores have been existing as an integral part of communities for centuries. However, the rise of e-commerce has resulted in their decline. With more and more people opting to shop online, traditional retailers are losing customers and business to e-retailers.
However, this does not mean that traditional retail will disappear from the market. Experts predict that the shops of the future will resemble showrooms more than brick-and-mortar stores. Traditional stores will then have to transform. In order to compete with e-shops effectively, traditional retail outlets will need to modify their space, bet on innovations, and change their role.
How to Get Started with E-commerce
Becoming an e-commerce seller doesn’t stop at having a digital storefront, whether a website or social media channel. You will have a lot of research to do, including the choice of products and services to offer, your target market, competition, and costs. Here’s a quick guide on how you can start your e-commerce business:
Conclusion
E-commerce redefined the way we shop. It grew even more since COVID-19, and over time, traditional brick-and-mortar stores will be more pressured to transform and keep up with the current demands.
But since it’s still a business, e-commerce can prove to be difficult to navigate, especially for beginners. While you can have a wider audience reach, you may encounter technical issues that can easily get out of control. Be sure to conduct in-depth research first before diving into the industry.